
AutoCAD for Architects | Essential Tools & Workflows
The Blueprint of Digital Design
AutoCAD is not just software; it is the foundational language of architectural communication. It is the primary tool for translating a conceptual design into a precise, technical set of instructions for construction.
While new tools handle 3D modeling and rendering, AutoCAD remains the industry standard for creating accurate, clear, and standardized 2D construction documents. Mastering its specific workflow is critical for any architect or drafter.
Why AutoCAD Endures in a 3D World
Despite the rise of BIM (Building Information Modeling) software like Revit, AutoCAD's role is secure. It is unparalleled for its speed and precision in creating detailed drawings. Think of it this way: BIM (Revit) is for building a digital model of the entire project, while AutoCAD is for drafting the specific views and details that come from that model. It is the go-to for:
- Detail Drafting: Creating intricate construction details for window sections, foundation connections, and roof assemblies.
- Site Plans: Drawing accurate property lines, grading plans, and landscape layouts.
- Schematic Design: Quick space planning and initial layout concepts.
- Coordination: Integrating drawings from other disciplines, like structural or MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) engineering.
The Architectural AutoCAD Workflow: Beyond Lines
Effective use of AutoCAD in architecture is not about drawing lines; it is about managing information. A messy drawing is unusable. A well-organized drawing is a powerful tool.
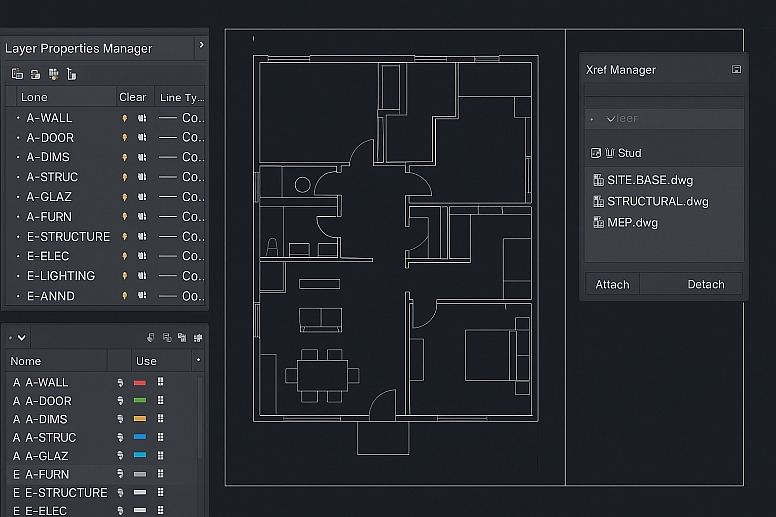
1. The Foundation: Layers and Standards: This is the most important concept for professional work. Every element in your drawing must belong to a specific layer.
- Purpose: Layers allow you to control visibility, line weights, colors, and plot styles. You can turn off furniture to see only walls, or isolate electrical plans.
- Naming Convention: Use a clear, standardized system like
A-WALLorA-DOOR. The prefix often denotes the discipline (e.g.,A-for Architectural,E-for Electrical). - AIA Standard: Many firms adhere to the American Institute of Architects (AIA) layer guidelines, which ensure consistency when sharing drawings between firms.
2. Precision is Non-Negotiable: Object Snaps and Tracking: Drawing "by eye" is unacceptable. AutoCAD's power lies in its ability to create geometrically perfect drawings.
- OSNAP (Object Snap): This feature allows you to snap to exact points like endpoints, midpoints, centers, and intersections. Always have relevant OSNAPs running.
- OTRACK (Object Snap Tracking): This allows you to align lines and points relative to other objects in the drawing, ensuring everything is perfectly aligned without construction lines.
3. Efficiency: Blocks and Xrefs: Reinventing the wheel wastes time. Smart architects reuse content.
- Blocks: A block is a grouped collection of objects that acts as a single entity. Create blocks for standard elements like doors, windows, toilets, and furniture. This allows you to insert them repeatedly, and editing one block updates all instances in the drawing.
- Xrefs (External References): This is a critical tool for collaboration. You can Xref another drawing (e.g., a structural grid or a site plan) into your current file. The referenced drawing is linked, not embedded. If the source file is updated, your file updates automatically. This keeps the architectural background, structural grid, and MEP plans perfectly synchronized.
Essential Commands for Architectural Drafting
While AutoCAD has hundreds of commands, a core set does most of the work.
| Command | Shortcut | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Line | L |
Drawing walls, objects, and lines. |
| Polyline | PL |
Creating a single object from connected line/arc segments. Essential for walls. |
| Offset | O |
Quickly creating parallel lines. Perfect for drawing walls of a specific thickness. |
| Trim / Extend | TR/EX |
Cleaning up intersections and making lines meet perfectly. |
| Hatch | H |
Adding material indicators like concrete, earth, or insulation to sections. |
| Dimension | DIM |
Adding accurate measurements. Use dimension styles for consistency. |
| Layer Properties | LA |
The command center for creating and managing your layers. |
From Digital to Physical: Layouts and Plotting
The final goal of an AutoCAD drawing is to be printed to scale.
- Model Space: This is your infinite digital drafting board where you draw everything at full scale (1:1). A wall is drawn 200 inches long, not 2 inches.
- Paper Space (Layouts): This is where you create your printable sheets. You create viewports, which are windows that look into your Model Space. Inside these viewports, you set the scale (e.g., 1/4" = 1'-0" for a floor plan).
- Plotting: This is the command for printing. Using CTB (Color-Dependent Plot Style Table) files, you assign line weights and colors to control how your drawing looks on paper, regardless of the colors on screen.
Beyond the Basics: Leveraging Advanced Tools
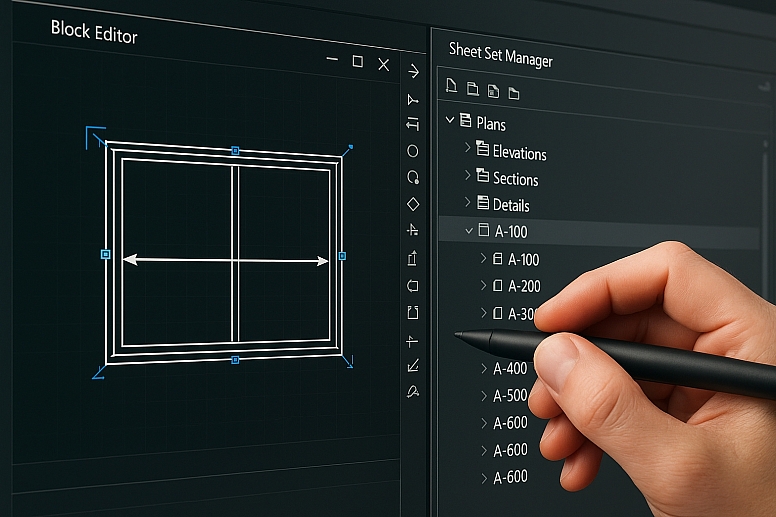
While core commands and layers form the foundation, mastering these advanced features will elevate your technical drawings:
- Dynamic Blocks: Create intelligent blocks with adjustable attributes (e.g., doors that stretch to fit wall thicknesses, windows with configurable panes).
- Sheet Sets: Manage multi-page drawing sets efficiently, automating page numbering, title blocks, and plotting.
- Data Extraction: Generate schedules (e.g., door/window schedules, material quantities) directly from drawing objects.
- Customization: Tailor AutoCAD with LISP routines or scripts to automate repetitive tasks, saving hours of manual work.
The Future of AutoCAD in Architecture
AutoCAD continues evolving alongside BIM and 3D workflows. Its future lies in:
- Cloud Collaboration: Using AutoCAD Web or AutoCAD with Fusion 360 for real-time team coordination.
- Interoperability: Seamlessly exchanging data with Revit, SketchUp, and other software via IFC or DWG formats.
- Automation: Integrating AI-driven tools for predictive design assistance and error detection.
Your Next Steps
- Practice Precision: Drill into commands like
OSNAP,XREF, andDIMSTYLEuntil they become instinctive. - Study Standards: Download the AIA Layer Guidelines or your local architectural standards to ensure industry compliance.
- Explore Integration: Experiment with linking AutoCAD drawings into Revit or Lumion for enhanced visualization.
The Drafting Board is Now Digital
AutoCAD is the modern architect's pencil. It requires the same discipline, precision, and understanding of drafting conventions that were used on a physical board. The tools are digital, but the principles of clear, unambiguous communication remain unchanged. Mastering its workflow is less about learning software and more about learning the language of construction.
Your design vision is only as strong as the documentation behind it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should I learn AutoCAD or Revit first? For a career in architecture, learning AutoCAD first provides a strong foundation in drafting principles, layer management, and construction documentation. This knowledge makes the transition to BIM software like Revit much smoother, as you understand what the software is automating.
Is AutoCAD used for 3D modeling? It has 3D capabilities, but they are rarely used for architectural practice. Software like Revit, SketchUp, and Rhino is far more efficient and powerful for architectural 3D modeling and BIM. AutoCAD's strength is in 2D.
How important is drawing standards and layering? It is everything in a professional environment. A drawing that does not follow the firm's or industry's standards is unusable for collaboration and construction. It is the mark of an amateur.
What is the biggest mistake beginners make? Drawing without using layers, object snaps, and a proper scale. This creates messy, inaccurate drawings that cannot be used for anything beyond a simple sketch.










